When we try to compare the fiber optic cable with copper cable, we may be thrown into trouble most of the time. Actually, it is too difficult to be impartial because the pros and cons between them are so clear. Apparently, fiber optic cable outweighs copper cable in the aspect of speed or bandwidth. It is much faster than copper cable, carries much higher bandwidth, has less interference and is lighter, stronger and more durable as well. Considering this situation, today we will just take a closer look at the advantages of fiber optic cable over copper cable.
It’s known the copper cable transmits data by electrical impulses, while fiber optic cable, which is made up by hair-like glass fibers, sends signals by carrying light impulses transmitted by a LED or laser. The infrared light inside the fiber optic cable would bounce at blistering speeds until it reaches the other end of the fibers. After the optical receiver receives the signals, then the signals would be converted into data. Since the fiber optic cable transmits data by lasers, the speed of it must be much higher than copper cable. In this text, fiber optic cable advantages such as bandwidth will be talked about in details below.
Speed here refers to the amount of data that can be transmitted per unit of time. Needless to say, fiber optic cable has a great win over copper cable in speed. For example, traditional copper lines can usually carry roughly 3,000 phone calls at one time, while fiber optic cables used in a similar system could carry around 31,000 calls.
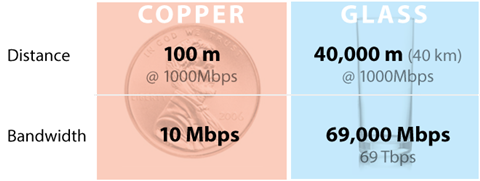
Unlike copper whose distance limitation is limited to 100m, fiber optic cable allows the distance to range 300m to 80km, depending on the style of cable, wavelength, and network. For instance, in Gigabit Ethernet (GbE) applications, multi-mode fiber (MMF), when used in combination with 1000BASE-SX SFPs (eg. MGBSX1) using 850nm wavelength, is able to realize 550m link length. Or other, when single-mode fiber (SMF) works in corporation with 1000BASE-LX SFP (eg. EX-SFP-1GE-LX) using 1310nm wavelength, the possible link length is 10km.
Bandwidth is the key point that determines the speed of the cables. Because of the higher bandwidth, fiber optic cable can have extremely high frequency ranges to carry data. This would be a thousand times the bandwidth of copper cable. If copper cable transmits data at high frequencies, it’s signal strength will diminish. Without any exaggeration, the fiber optic cable can go more than one hundred times further, while the copper cable could only hold a candle.
Fiber optic cable permits extremely reliable data transmission. Because the core is made of glass, which is an insulator, no electric current can flow through a fiber optic cable. Besides, fiber immune to many environmental factors that have effects on copper cable, immune to electromagnetic interference and radio-frequency interference (EMI/RFI), crosstalk, impedance problems, and more. You can run fiber next to industrial equipment without worry. In addition, fiber is also less susceptible to temperature fluctuations than copper is, and it can be submerged in water. More importantly, fiber optic cable can carry more information with greater fidelity than copper wire can. That’s why telephone and CATV companies are converting to fiber.
Fiber optic systems are already being used in the backbone applications of most major companies because of their reliability and upgradability. All up, it is fairly safe to assume that, just as digital telephony has done in the past, so fiber optic technology will move ahead with big steps leaving the traditional copper wire behind.

Post a Comment